Brain
Expert Pharmacologist
- Joined
- Jul 6, 2021
- Messages
- 290
- Reaction score
- 315
- Points
- 63
2-Fluorodeschloroketamine (2-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexan-1-one) - is a dissociative anesthetic (structural analog of
 ketamine) belonging to the class of arylcyclohexylamines. When used, it most often causes impairment of consciousness, agitation and hallucinations. It has similar reinforcing and discriminative effects as ketamine. 2F-DCK is a new psychoactive ketamine derivative that has been found in sewage treatment plants. Various sporadic clinical reports describe the use of this psychoactive substance to induce a dissociative state and reveal concentrations in the high range (human biological samples). However, 2F-DCK is not controlled or regulated in many countries. 2-FDCK belongs to a class of compounds called arylcyclohexylamines which contains various other drugs such as PCP and ketamine. Their general structure consists of a cyclohexylamine unit with an aryl group attached to the same carbon as the amine. 2-FDCK has an o-fluorophenyl group as an aryl substituent and the amine group is methylated. The cyclohexyl ring features a ketone group next to the amine position.
ketamine) belonging to the class of arylcyclohexylamines. When used, it most often causes impairment of consciousness, agitation and hallucinations. It has similar reinforcing and discriminative effects as ketamine. 2F-DCK is a new psychoactive ketamine derivative that has been found in sewage treatment plants. Various sporadic clinical reports describe the use of this psychoactive substance to induce a dissociative state and reveal concentrations in the high range (human biological samples). However, 2F-DCK is not controlled or regulated in many countries. 2-FDCK belongs to a class of compounds called arylcyclohexylamines which contains various other drugs such as PCP and ketamine. Their general structure consists of a cyclohexylamine unit with an aryl group attached to the same carbon as the amine. 2-FDCK has an o-fluorophenyl group as an aryl substituent and the amine group is methylated. The cyclohexyl ring features a ketone group next to the amine position.
 The chemical structure of 2-FDCK differs from ketamine only in that there is a fluorine atom attached to the phenyl group. Ketamine has a chlorine atom in that position. 2-FDCK was synthesized by a team of chemists in the Nuclear Medicine Department of The Educational, Research and Clinical Center in 2013 as part of the second phase of research and evaluation of new anesthetics for fluorinated derivatives of ketamine and its analogues. As early as 2020, Xue-Ting Shao conducted a study that first described detected 2F-DCK in wastewater samples collected from nine wastewater treatment plants in seven major Chinese cities between 2018 and 2020 using the epidemiological study (WBE). In a study by Li and Huskinson, 2F-DCK was shown to induce self-administration, generalize to discriminatory ketamine stimuli, and induce conditional place preference in rats and self-administration of ketamine or 2F-DCK determines their functions as reinforcers but does not provide quantitative information about their reinforcing effectiveness; preclinical data have shown reinstatement of ketamine-seeking behavior induced by cues and ketamine priming after ketamine self-administration, however, to date, the reinforcing effectiveness and reinstatement of drug seeking by 2F-DCK are still unclear. In 2016, after issuing its annual sales report, the EMCDDA formally notified for the first time that controls were in place for the substance.
The chemical structure of 2-FDCK differs from ketamine only in that there is a fluorine atom attached to the phenyl group. Ketamine has a chlorine atom in that position. 2-FDCK was synthesized by a team of chemists in the Nuclear Medicine Department of The Educational, Research and Clinical Center in 2013 as part of the second phase of research and evaluation of new anesthetics for fluorinated derivatives of ketamine and its analogues. As early as 2020, Xue-Ting Shao conducted a study that first described detected 2F-DCK in wastewater samples collected from nine wastewater treatment plants in seven major Chinese cities between 2018 and 2020 using the epidemiological study (WBE). In a study by Li and Huskinson, 2F-DCK was shown to induce self-administration, generalize to discriminatory ketamine stimuli, and induce conditional place preference in rats and self-administration of ketamine or 2F-DCK determines their functions as reinforcers but does not provide quantitative information about their reinforcing effectiveness; preclinical data have shown reinstatement of ketamine-seeking behavior induced by cues and ketamine priming after ketamine self-administration, however, to date, the reinforcing effectiveness and reinstatement of drug seeking by 2F-DCK are still unclear. In 2016, after issuing its annual sales report, the EMCDDA formally notified for the first time that controls were in place for the substance.


Basic aspects of synthesis: 0.05 mol (10.4 gr) of α-hydroxycyclophenthyl-(2-flourophenyl)-N-methylamine was dissolved in 85 mL of decalin followed by the addition of 0.25 gr PdCl2 (3 mol%) and was refluxed for 4 h. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and the residue was extracted with 160 ml of hydrochloric acid (10 %). To this acidic solution 80 mL NaOH (50 %) was added, followed by the addition of 120 ml of chloroform. The organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted twice with 25 mL of chloroform. The combined organic phase was dried on MgSO4. The insoluble material was filtered off and the organic solvent evaporated under reduced pressure to afford 5.5 gr (53%) pure brown oily fluoro ketamine.Read more about synthesis:
Ketamine synthesis from 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxycyclohexanone
Introduction In this method, imiеation of (1) was carried out by the reaction of this compound with methylamine. The reaction was carried out in the presence of 0.04 g of potassium carbonate and in the dark and solvent-free conditions. Finally, thermal rearrangement of (2) produced ketamine (3)...
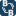 bbgate.com
bbgate.com
Ketamine precursor synthesis
Introduction 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-2-hydroxycyclohexanone (cas 1823362-29-3) is a precursor in simple Ketamine synthesis. This synthesis has less step than classical Ketamine synthesis from cyclopentyl bromide and o-chlorobenzonitrile and a little bit bigger yield. Moreover, you can ship...
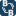 bbgate.com
bbgate.com
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics
2F-DCK, like ketamine, undergoes a fairly extensive metabolism. Initially, the active metabolite nor-2F-DCK is formed through
Oral bioavailability of fluoroketamine is only 25-35%, and peak concentrations are reached within 15-75 minutes, which is associated with intensive liver metabolism during the first passage of the substance. Intranasal and intrarectal bioavailability ranges from 45% to 65%. Fluoroketamine is rapidly distributed in tissues with high perfusion capacity including the brain and binds to plasma proteins from 10% to 50%, which explains a large volume of distribution of 3-5 l/kg. The elimination half-life is about 69 minutes (in in vitro studies) with a CLint of ≤ 5.88 mL/min/kg. Theoretically, when administered intravenously, 2F-DCK will have a half-life of approximately 250 minutes with a total clearance of approximately 15 ml/min. About 85-95% of 2F-DCK metabolites are excreted in urine, low concentrations of 2F-DCK are excreted in bile and feces. 2F-DCK, like ketamine, is distributed mainly in the cerebral cortex, and its N-demethylated metabolites in the cerebellum and kidneys. No information on the quantitative concentrations of fluoroketamine in other bodily fluids is available at this time.
The mechanism of action of 2-FDCK is almost identical to that of ketamine. 2-fluorodeschloroketamine (similar to ketamine)binds
Clinical effects of ketamine
As for the desirable positive effects of recreational use of 2-fluorodeschloroketamine, it has a moderate or pronounced sedative effect. Extremely pronounced effects related to "spontaneous bodily sensations", with an increase in the dose, are leveled. Euphoria from 2-fluorodeschloroketamine use is described as slight or moderate. At high doses, general motor activity and motor skills are disrupted, in proportion to the increase in dose, "Optical sliding" effects appear, dizziness, the level of anxiety decreases up to its complete absence (however, with the dose increased, anxiety level can increase as well. In some users anxiety level can build up even when using low doses. This is an indication for discontinuation of use). At low and medium doses, the effects of "Conceptual thinking", "Immersion enhancement", "Increased music appreciation" and "Introspection" occur. The appearance of various sound and optical illusions are also considered positive by users. "Existential self-realization" and "Spirituality enhancement" are subjective personal effects of 2-fluorodeschloroketamine. With 2-FDCK used, blood pressure increases by an average of 25%, and the heart rate increases by 20%, as well as cardiac output and oxygen consumption by the myocardium. The positive inotropic effect is associated with an increase in the internal calcium flow modulated by cAMP. 2-FDCK can significantly increase the pressure in the pulmonary artery, pulmonary vascular resistance and intra-pulmonary shunt. Hemodynamic effects of 2-FDCK are not dose-dependent, and repeated administration of this substance causes less or even opposite effects. It is likely that the mechanism of the changes above is due to the fact that 2-FDCK suppresses the function of baroreceptors through the effect on the NMDA receptors of the nucleus tractus solitarii, as well as due to the sympathetic-neuronal release of norepinephrine.
Negative undesirable effects of 2-fluorodeschloroketamine recreational use include: pronounced sedation up to deep deafening and coma, complete loss of control over motor skills and consciousness, hypersalivation, nausea and vomiting, decreased libido, physical autonomy, impaired urination up to the complete impossibility of emptying the bladder (in some cases, cystitis, hydronephrosis, dysuria, the appearance of blood in the urine and other similar pathology associated with the urinary system, which is one of the main forms of 2-fluorodeschloroketamine toxicity, especially with prolonged use); there is also depersonalization and derealization, frequent deja vu (some users attribute this symptom to positive effects), the impossibility of logical and abstract thinking, confusion, inability to focus on a specific task, short-term memory impairment (with high doses - complete retrograde amnesia), suppression of personal prejudices, psychosis, synesthesia, spatial and temporal disorientation, distortion of the sense of time, pronounced auditory and visual hallucinations (true and false).
Hallucinations are the most frequent and, at medium and high doses, are described as bright, fast-moving colorful and complex geometric patterns, or constants of shape, fractals and colors, organized or disorganized, structureless or structural, located far beyond the perception of the user's thoughts, can be accompanied by visual noise, bright flashes, images of real people, objects. When using 2-fluorodeschloroketamine, addiction can be developed; however, its potential is quite low and remains at the psychosomatic level without physical manifestations. Also, side effects of 2-fluorodeschloroketamine use include: anaphylactic reactions (rarely) and hypersensitivity reactions, anorexia (with prolonged use), delirium, "flashbulb" symptom, dysphoria, insomnia, diplopia, nystagmus, increased skeletal muscle tone and tonic-clonic seizures, increased intraocular pressure, bradycardia, arrhythmia, laryngospasm, increased frequency of respiratory movements (with induction doses).
Methods of use and doses
When administered orally, 2F-DCK doses vary from 0.5 mg/kg to 2 mg/kg. Such way of administration helps to avoid irritation of the nasal mucosa, pain (2-fluorodeschloroketamine (damages nasal mucosa more than ketamine). It is advisable to use capsules (if ketamine is in form of powder). The duration of action with oral administration is on average 4-5 hours, and the onset of action gradually begins after 10-20 minutes.
When administered intranasally, effects manifest after 5-15 minutes and have a total duration of up to two hours (on average 4-5.5 hours). With this way of administration it is easy to monitor and control one`s condition and frequency of use. Starting (low) dose of 2F-DCK is 0,1-0,4 mg/kg, medium dose is 0,5-1 mg/kg. Doses more than 1.5 mg/kg are considered as high and increase the risk of side effects, hallucinations, retrograde amnesia and loss of consciousness with respiratory depression.
When administered parenterally (intravenously and intramuscularly), doses start from 0,05 mg/kg and provide particular subjective feelings during 2F-DCK trip. However, in case of increasing the dose, there is a risk of getting general anaesthesia at the tip of the needle, which is characterized by retrograde amnesia and inability to recall the feeling of 2F-DCK trip, which is why thorough titration or low starting dose are advised.
Special instructions, dangerous interactions with other substances
2F-DCK is not recommended for recreational use by people with thyroid gland diseases, kidneys, mental disorders, infectious diseases, brain tumors or contusions, chronic severe (or moderate) diseases of the cardiovascular system, lungs, liver and kidneys. When 2F-DCK is used together with ethanol, phenothiazines, antihistamines, any sleeping pills, it may worsen the depression of the central nervous system, which increases the risk of developing central respiratory failure.
Special instructions, dangerous interactions with other substances
2-fluorodeschloroketamine is not recommended for recreational use by people with thyroid gland diseases, kidneys, mental disorders, infectious diseases, brain tumors or contusions, chronic severe (or moderate) diseases of the cardiovascular system, lungs, liver and kidneys. When 2-fluorodeschloroketamine is used together with ethanol, phenothiazines, antihistamines, any sleeping pills, it may worsen the depression of the central nervous system, which increases the risk of developing central respiratory failure.
Low risk when used together with 2-fluorodeschloroketamine (or amplification of 2-fluorodeschloroketamine effects): mushrooms, LSD, DMT, DOx, NBOMes, cannabis, MDMA, Mescaline, DXM, SSRIS, caffeine.
High risk when used together with 2-fluorodeschloroketamine: amphetamines, Cocaine, Benzodiazepines, MAOIs, 2C-x, 2C-Tx, aMT, 5-MeO-xxT, MXE, PCP, N20.
Extremely high risk when used together with 2-fluorodeschloroketamine: alcohol, GHB/GBL, opioids, tramadol.
In people taking a course of hormone therapy recreational use of 2-fluorodeschloroketamine in any doses is not recommended due to the high risk of increased blood pressure. In some cases after intake of a high 2-FDCK dose, there may be a depressive state, short-term and long-term memory impairement (including verbal and visual). This cognitive deficit recovers for some time without pharmacological therapy. Absolute contraindications for 2-FDCK use are: severe cardiovascular diseases (for example, uncontrolled hypertension or unstable angina), uncontrolled psychosis or schizophrenia, pregnancy at any term, severe liver diseases (cirrhosis, active hepatitis of any etiology, hepatocellular carcinoma, and so on).
