- Language
- 🇺🇸
- Joined
- Nov 16, 2023
- Messages
- 373
- Reaction score
- 290
- Points
- 63
Can anyone help me understand if it is possible to use generic nasal inhalers that contain "levmetamfetamine 50mg" to get to d-meth.
https://bbgate.com/threads/methamphetamine-synthesis-vicks-inhaler.4974/#post-46343 Will these instructions work in theory?
Or do I need to use the above racemization and resolution provided by Amphibian? Or 41Dxflatline, etc?
https://bbgate.com/threads/methamphetamine-synthesis-vicks-inhaler.4974/#post-46343 Will these instructions work in theory?
Or do I need to use the above racemization and resolution provided by Amphibian? Or 41Dxflatline, etc?
While it would work... some of those chemicals are hard to get or might be dangerous like my username, instead you should use naproxen and use the pope-peachy with the NASID Naproxen. I have posted the full guide below
↑View previous replies…
- By azides
The workup has been posted earlier but again
It is ....
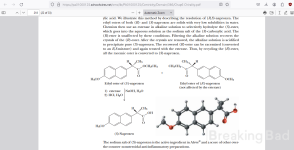
Study of the mechanism of the optical resolution of N-methylamphetamine via diastereoisomeric salt formation by the Pope-Peachey resolution method as discussed by the retort later
https://sci-hub.wf/10.1016/s0957-4166(00)86170-4
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0957416600861704
refences and Notes
I.) Newman,P. Optical Resolution Procedures for Chemical Compounds, vols.l-3, optical Resolution Informztion
Catre, Manhattan College, New York, 1978-84;
2.) Jacques,J.; Collet,A.; Wilen,SH. Enantiomers, Racemates and Resolutions, Wiley and Sons, New York,
1981,378.p.
3.) Fogassy,E.; hs,M.; Faigl,F ; Rohonczy,J, Ecsery,Z. J.Chem.Soc.Perkin Trans.2, 1986, 1881
4.) Pope,W.J.; Peachey,S.J. J.Chem.Soc.,1899,75,1066
5.) 7.84 g (0.0525 mol) racemic N-methylamphetamine and 9.73 g (0.0525 mol) racemic N-
methylamphetamine hydrochloride were dissolved in 70 ml of abs. ethanol and 7.91 g (0.0525 mol) R,R-
tartaxic acid in 56 ml of abs. ethanol. Both stock solutions were divided into fifteen portions by volume by a
burette and reacted at 22+1”C The mixtures were standii undisturbed for 15, 90 minutes and 5, 24, 1 IS
hours, than the precipitates were filtered and dried. From 0.4 g of each salt the base was liberated by ccNaOH
and extracted from the aqueous phase by dicblorometbane.
6.) All experiments were performed at the same work-bench at 2Ul’C room temperature. Stock solutions of
the racemate and the resolving agent were used to avoid the error of weight measurements. All the flasks used
had identical size and shape
7.)The tartrate and hydrochloride content of the salts were determined by potenciometry by a RADIOMETER-
85 TTT automatic titrator with 0.1 N NaOH and 0.1 N AgNO,.
8.) The specific rotations was measured by a Perkin Elmer 241 polarhneter. The specific rotation of the
optically pure R-N-methylamphetamine is [a]: - -18.90 (c 0.1, IN HCI).
9.) The salts were not washed at filtering. The small amount of hydrochloride found in the salts probably comes
from the mother liquor sticked and dried to the surface of the salt.
10.) This is in accordance with the results3, that the R-l II is the more stable salt than S-1.11
If you want more you could also read the retort below everything should be in the https://sci-hub.wf by in large though
Instead in this twist , only half an equivalent of chiral amine is used. Half an equivalent of a cheaper, optically inactive amine base is used in its place. This not only makes the process cheaper, but results in a more dramatic difference in solubilities. The conjugate base of the desired (d)-(+)-enantiomer crystallizes out with the conjugate acid of the chiral amine, with high selectivity. This leaves the more soluble salt product of (l)-(-)-naproxen and the achiral amine behind in solution.
It is ....
Study of the mechanism of the optical resolution of N-methylamphetamine via diastereoisomeric salt formation by the Pope-Peachey resolution method as discussed by the retort later
https://sci-hub.wf/10.1016/s0957-4166(00)86170-4
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0957416600861704
refences and Notes
I.) Newman,P. Optical Resolution Procedures for Chemical Compounds, vols.l-3, optical Resolution Informztion
Catre, Manhattan College, New York, 1978-84;
2.) Jacques,J.; Collet,A.; Wilen,SH. Enantiomers, Racemates and Resolutions, Wiley and Sons, New York,
1981,378.p.
3.) Fogassy,E.; hs,M.; Faigl,F ; Rohonczy,J, Ecsery,Z. J.Chem.Soc.Perkin Trans.2, 1986, 1881
4.) Pope,W.J.; Peachey,S.J. J.Chem.Soc.,1899,75,1066
5.) 7.84 g (0.0525 mol) racemic N-methylamphetamine and 9.73 g (0.0525 mol) racemic N-
methylamphetamine hydrochloride were dissolved in 70 ml of abs. ethanol and 7.91 g (0.0525 mol) R,R-
tartaxic acid in 56 ml of abs. ethanol. Both stock solutions were divided into fifteen portions by volume by a
burette and reacted at 22+1”C The mixtures were standii undisturbed for 15, 90 minutes and 5, 24, 1 IS
hours, than the precipitates were filtered and dried. From 0.4 g of each salt the base was liberated by ccNaOH
and extracted from the aqueous phase by dicblorometbane.
6.) All experiments were performed at the same work-bench at 2Ul’C room temperature. Stock solutions of
the racemate and the resolving agent were used to avoid the error of weight measurements. All the flasks used
had identical size and shape
7.)The tartrate and hydrochloride content of the salts were determined by potenciometry by a RADIOMETER-
85 TTT automatic titrator with 0.1 N NaOH and 0.1 N AgNO,.
8.) The specific rotations was measured by a Perkin Elmer 241 polarhneter. The specific rotation of the
optically pure R-N-methylamphetamine is [a]: - -18.90 (c 0.1, IN HCI).
9.) The salts were not washed at filtering. The small amount of hydrochloride found in the salts probably comes
from the mother liquor sticked and dried to the surface of the salt.
10.) This is in accordance with the results3, that the R-l II is the more stable salt than S-1.11
If you want more you could also read the retort below everything should be in the https://sci-hub.wf by in large though
Instead in this twist , only half an equivalent of chiral amine is used. Half an equivalent of a cheaper, optically inactive amine base is used in its place. This not only makes the process cheaper, but results in a more dramatic difference in solubilities. The conjugate base of the desired (d)-(+)-enantiomer crystallizes out with the conjugate acid of the chiral amine, with high selectivity. This leaves the more soluble salt product of (l)-(-)-naproxen and the achiral amine behind in solution.
Last edited: